Instruction
Some of the key words used in this module are explained below. You can print these to use as you work through the module.
App – Short for application. A digital tool used on a smartphone or tablet to do a specific task.
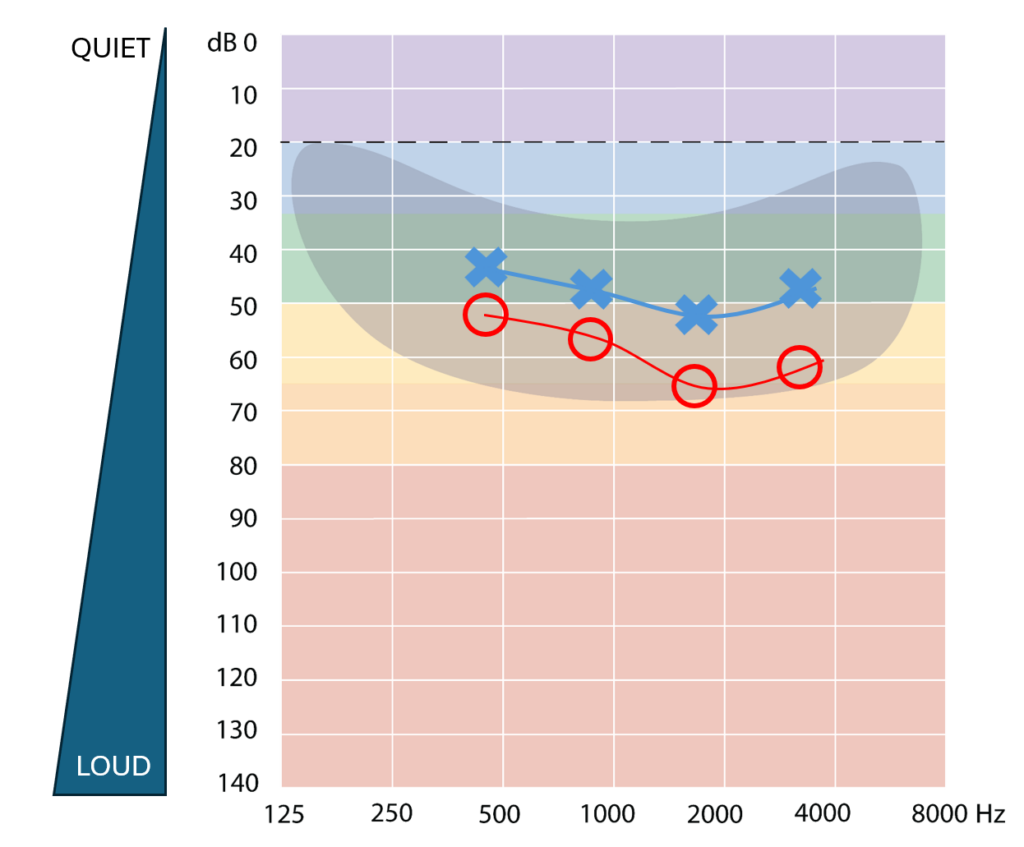
Audiogram – A graph of a person’s hearing showing the quietest sound a person can hear (hearing threshold) at different frequencies of sound.
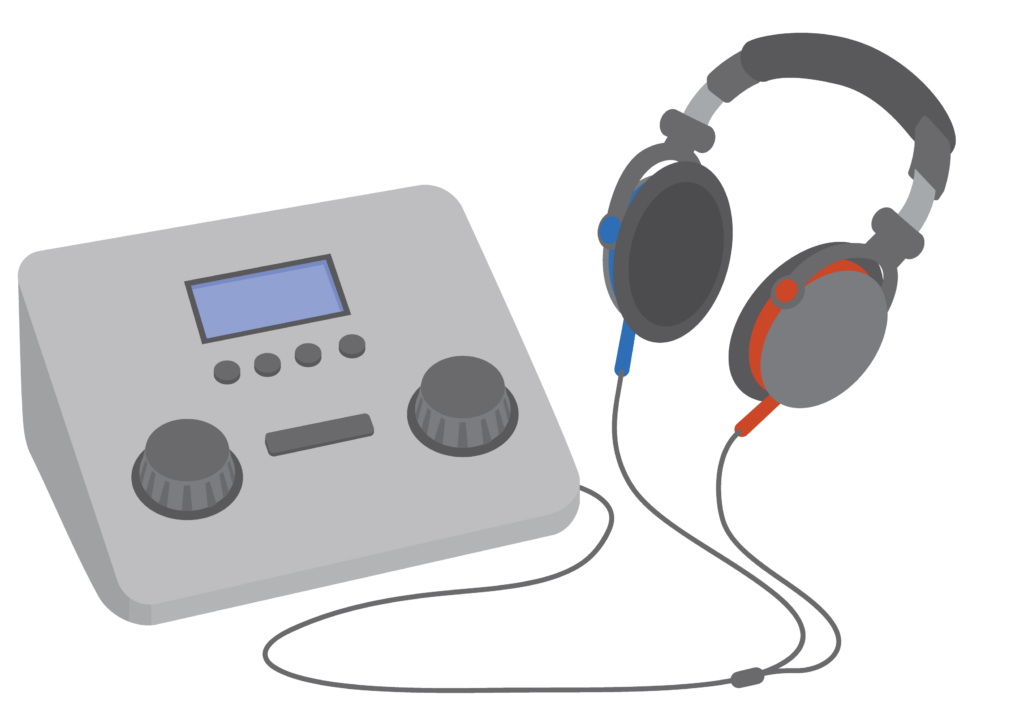
Audiometer – Hearing test device used to measure hearing.

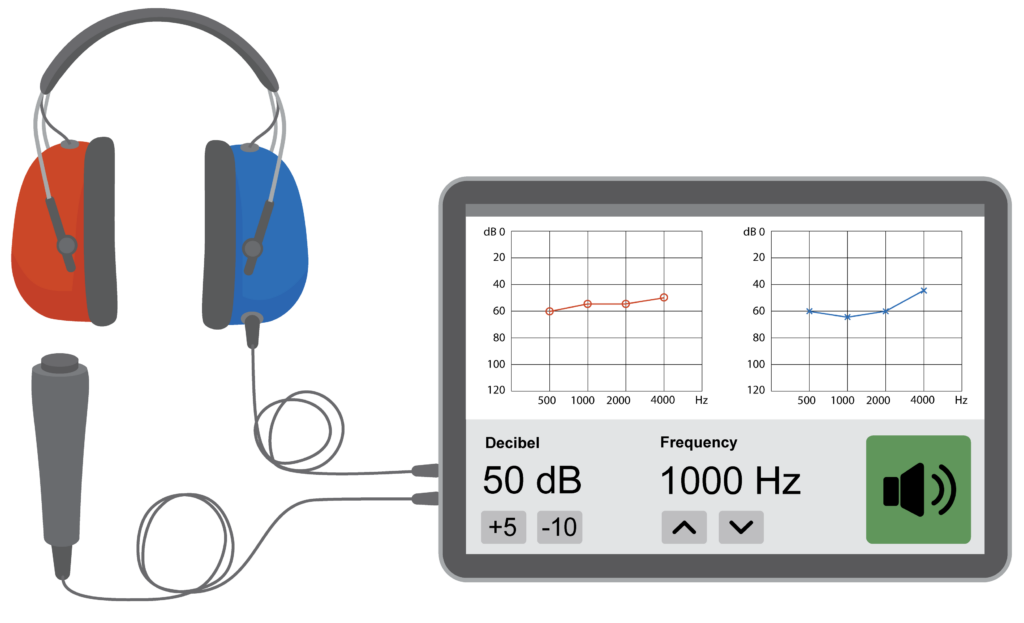

Audiometry (hearing test) – A test of how well a person can hear. If there is any hearing loss, the results show the level of loss.
Average hearing threshold – A calculation adding threshold values of 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, and 4000 Hz then dividing by four.
Ear and hearing professional – Professionals that test, manage, and treat ear and hearing problems.
Feedback (whistling) – The “whistle” sound produced by the hearing aid when sound escapes from the ear and is picked up by the microphone of the hearing aid.
Frequency – How many times a sound wave moves up and down in one second. There are different types of sound including deeper sounds (low frequency) such as a drum and sharper sounds (high frequency) such as a whistle. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz).
Hard of hearing – A term used for a person with mild to severe hearing loss, who cannot hear as well as a person with normal hearing.
Hearing threshold – Quietest sound that the person can hear at different frequencies of sound.
Hertz (Hz) – A way to measure how often something happens in one second. For example, if a sound wave vibrates 100 times in one second, it has a frequency of 100 Hz.
Ling sounds – A set of six sounds. These cover the full range of speech sounds across low to high frequencies.

Standard earmould – A ready-made shaped earpiece produced in different sizes to fit inside a person’s ear. It connects to the hearing aid through a tube and delivers sound into a person’s ear.
Stetoclip (listening tube) – Also known as a listening tube, it allows a person with normal hearing to monitor if the hearing aid is working well.

Instruction
If you find other words that you are not familiar with, ask a colleague or your mentor.