A hearing test will measure a child’s right and left ears to check for hearing loss. The results will help you, the child and their caregiver decide if hearing aids could help.
Instruction
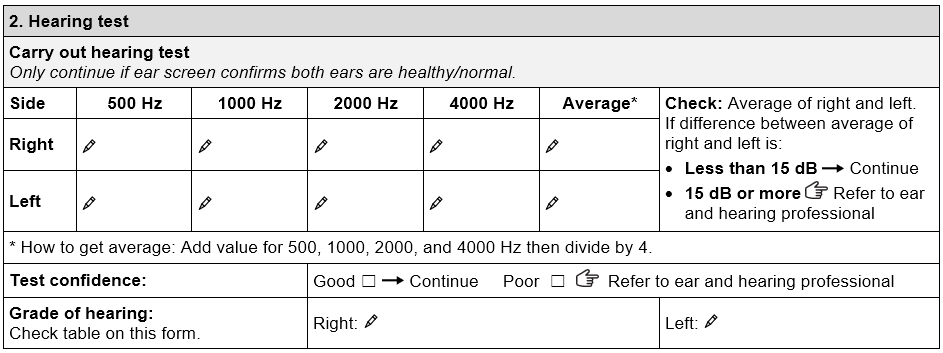
Use the hearing test section of the assessment form and check the Grade of hearing loss table to find out if a child has any hearing loss.
Question
What could you do to make it easier for a child with hearing loss to understand what you are saying?
Select two.
If you selected c and d, you are correct!
Sit at the same level as the child. Keep your face in good light while speaking clearly and slowly to make it easier for them to understand what you are saying.
Child-friendly approach
Prepare a child for the hearing test in a simple, fun and playful way.
Show the equipment so they know what will happen during the hearing test.
Instruction
Watch this video of a health worker using a child-friendly approach to explain a hearing test.
Question
Look at this picture of a health worker showing equipment using a child-friendly approach.
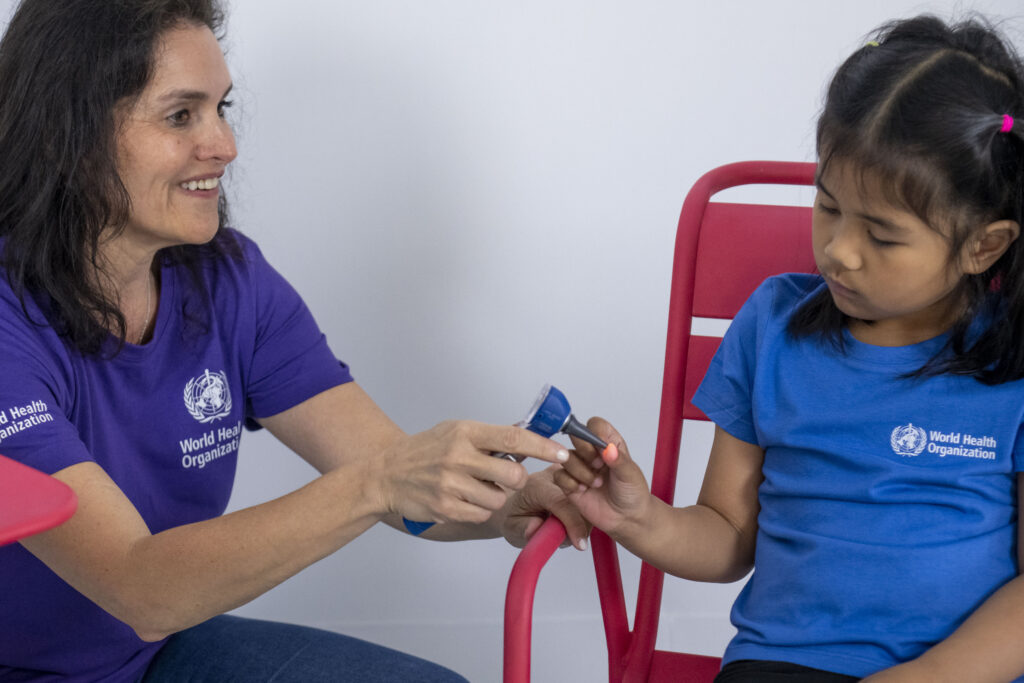

1. What makes this approach child-friendly?
- Sitting at the child’s level
- Smiling and looking at the child
- Letting the child see the equipment.
2. What are some other ways to reassure a child during a hearing test?
Other ways to reassure a child include:
- Using a friendly voice
- Explaining things slowly and checking that the child has understood
- Telling the child they are doing well.
Carrying out a hearing test
When carrying out a hearing test with a child:
- Explain the hearing test
- Practice test response
- Carry out hearing test
- Calculate average hearing threshold
- Record result for each ear.
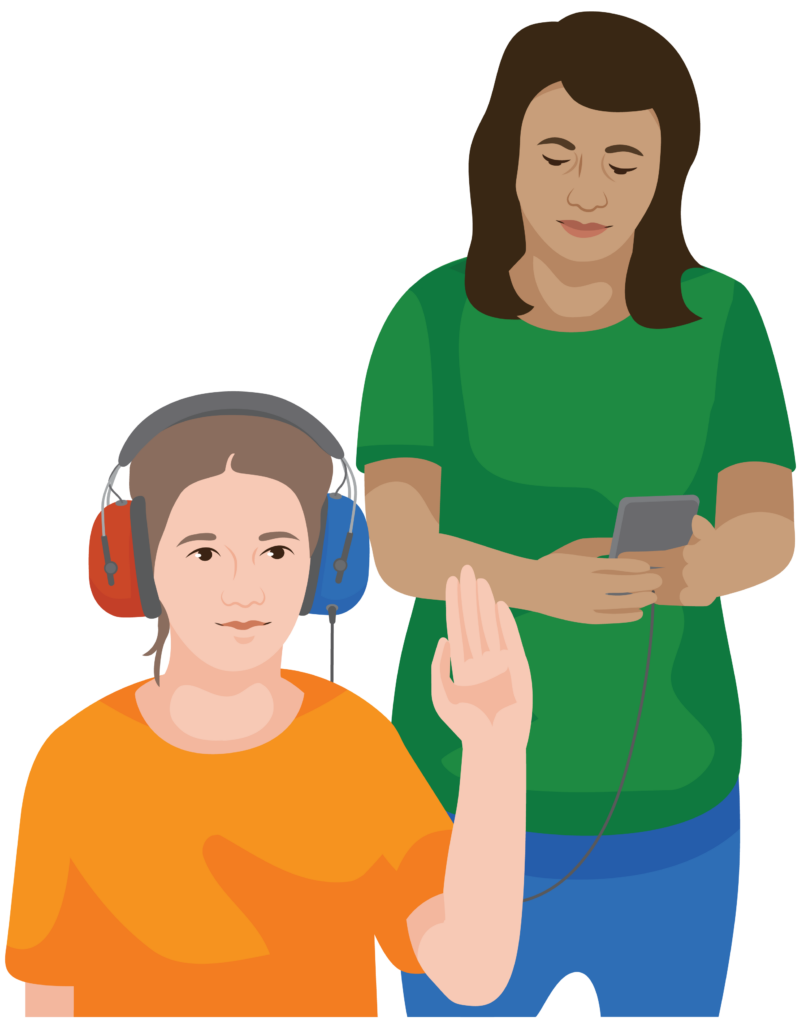

1. Explain the test
Explain that you will test the child’s hearing by measuring the quietest sound that they can hear (hearing threshold).
2. Practice test response
Sit opposite the child so they can see you clearly.
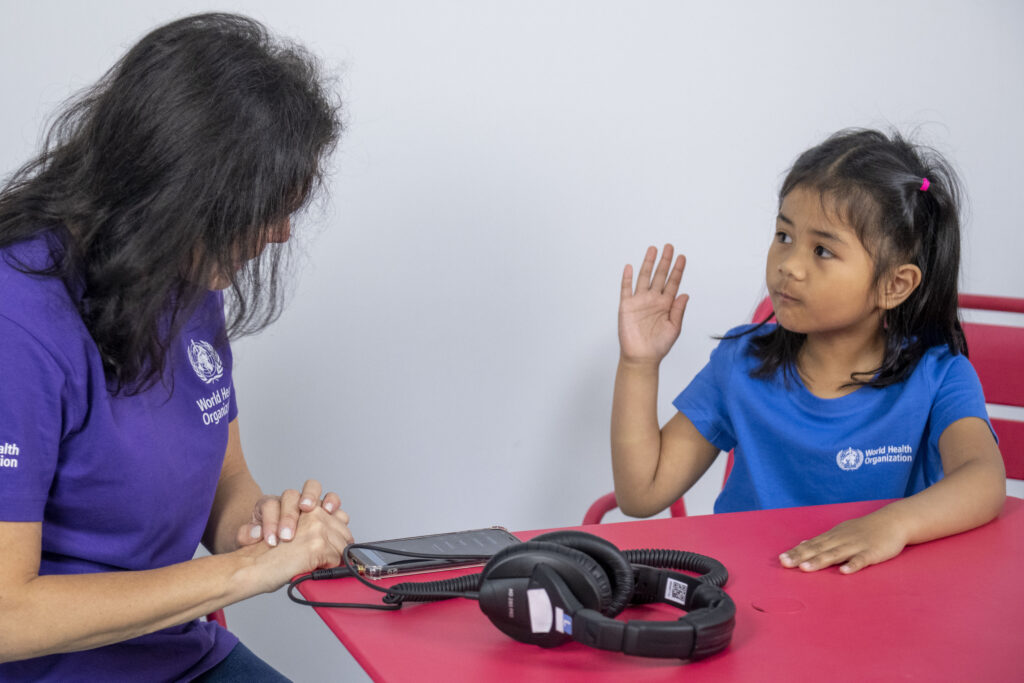

Explain:
- As soon as you hear the sound, press the response button or raise your hand on the same side as the sound
- Release the button or lower your hand as soon as you no longer hear the sound
- Before putting on the headphones practice the test response
- When the child responds, praise and encourage them.
Tip
If the child does not respond to the test it may help to:
- Use toys or stickers to encourage the child to participate
- Change the response signal, for example, the child waves their hand or drops a toy when they hear the sound
- Demonstrate with their caregiver
- Show them a video of another child doing the task.
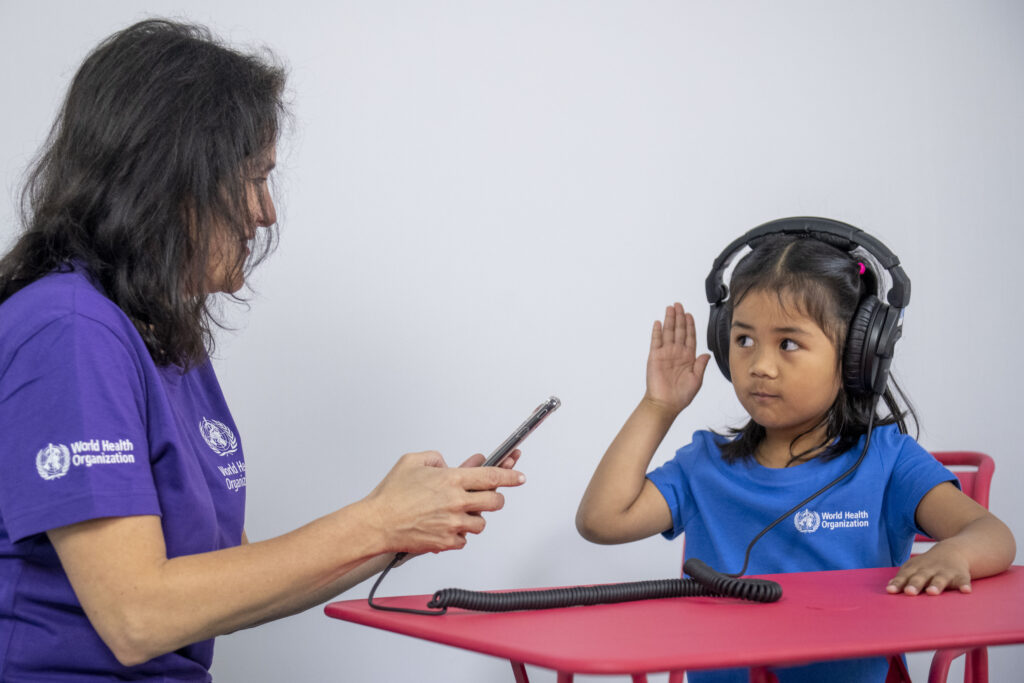

Practice with the child first at 1000 hertz (Hz) and 40 decibels (dB):
- Ask the child to put on the noise cancelling headphones
- Check headphones are in the correct position
- Practice twice in each ear.
Tip
If the child cannot hear the practice sound, increase the loudness by 10 dB and repeat.
3. Carry out hearing test
- Put the noise cancelling headphones on the child
- Check headphones are in the correct position
- Start test on the child’s better hearing ear – if better hearing ear is not known, start with their right ear
- Set frequency dial at 1000 Hz and intensity at 40 dB.
Tip
For more accurate testing:
- Position yourself so the child cannot see you presenting the sound
- Change the rhythm of how you present the sounds. This is to avoid them guessing when you will present the next sound.

Higher frequency sounds of 1000 Hz are usually easier to hear and give a child confidence at the start of a hearing test.
- Press the button for 2 to 3 seconds and see if the child raises their hand:
- If the child raises their hand, reduce the intensity level by 10 dB
- If the child does not respond, increase the intensity level by 5 dB
- Continue until you find the quietest sound the child can hear:
- Repeat the sound three times to confirm hearing threshold
- If the child responds correctly at least two out of three times at the frequency tested, record threshold on form
- Repeat for testing at 2000 Hz, 4000 Hz and 500 Hz
- Repeat on the child’s left ear.
Instruction
Watch this video of a child having a hearing test.
Activity
In groups practice carrying out a hearing test with a child who does not have hearing loss.
Prepare:
- Identify a space
- Check sound level is suitable using a sound level meter or downloaded hearWHO app:
- Click on ‘check your hearing’ to access sound level meter
- Allow permission to measure noise.
Test:
- Explain the test in a child-friendly way
- Carry out the test at 1000, 2000, 4000 and 500 Hz on child’s better hearing ear or right ear
- Record the quietest sound the child can hear for each frequency
- Repeat on the other ear.
Test confidence
When carrying out a hearing test, consider how confident you are about the test results.
You may have confidence if the child:
- Responds consistently to the presented sounds
- The hearing threshold for each frequency is identified.
You may have little or no confidence if the child:
- Randomly responds to presented sounds
- Responds even when no sound is presented
- Only responds when they see the tester move.
If you have good test confidence, continue.
If you have poor test confidence after discussing with your mentor refer person to ear and hearing professional.
Warning
Accurate test results are important for the correct programming of hearing aids.
4. Calculate average hearing threshold
- Get the average dB by adding threshold value of 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, and 4000 Hz then divide by four.
- Compare the threshold average of the right and left ear:
- Less than 15 dB difference Continue
- Difference of 15 dB or more Refer to ear and hearing professional.
For children with unilateral (one sided hearing loss) and asymmetrical hearing loss (right and left average thresholds different by more than 15 dB), their needs are more complex. Refer to ear and hearing professional.
Instruction
Answer the following questions to test your knowledge from the TAP Preprogrammed hearing aids module.
Question

Meet Anju
Anju is six years old and goes to school.
Anju has received treatment for an ear infection. She returns with her parents to the local health centre for an ear health check and hearing test.
The health worker carries out an ear health screen. Both her ears are healthy. They continue with a hearing test. Anju responds confidently during the hearing test.
Look at her hearing thresholds for each frequency.
| Side | 500 Hz | 1000 Hz | 2000 Hz | 4000 Hz |
| Right | 15 | 10 | 20 | 10 |
| Left | 10 | 10 | 15 | 15 |
1. What is the correct average hearing threshold for Anju’s right ear?
13.75 dB is correct!
It is the average of adding all the numbers and dividing by four.
2. What is the correct average hearing threshold for Anju’s left ear?
12.50 dB is correct!
It is the average of adding all the numbers and dividing by four.
3. Does Anju have less than 15 dB difference between her right and left ears?
Select one.
Yes is correct!
The difference is less than 15 dB. You can continue.
Check the Grade of hearing loss table on the assessment form or below.
| Grade | Average |
| Within normal range | Average of less than 20 dB |
| Mild hearing loss | Average of 20-34 dB |
| Moderate hearing loss | Average of 35-49 dB |
| Moderately severe hearing loss | Average of 50-64 dB |
| Severe hearing loss | Average of 65-79 dB |
| Profound hearing loss | Average of more than 80 dB |
4. What is the grade of hearing loss for Anju’s right ear?
Select one.
Normal hearing range is correct!
13.75 dB is in the normal hearing range.
5. What is the grade of hearing loss for Anju’s left ear?
Select one.
Normal hearing range is correct!
12.50 dB is in the normal hearing range.
5. Record result for each ear
- Write the average hearing values on the hearing test section of the form
- Record test confidence
- Record grade of hearing for right and left ear.
Follow the recommended action for the level of hearing loss found in the Grade of hearing loss table.
Explain test results
After completing the hearing test and identifying the grade of hearing loss, explain results and whether the child may benefit from hearing aids.
Remember Anju?

You explain the results of Anju’s hearing test to Anju and her parents. Anju’s hearing is normal. She does not require hearing aids.