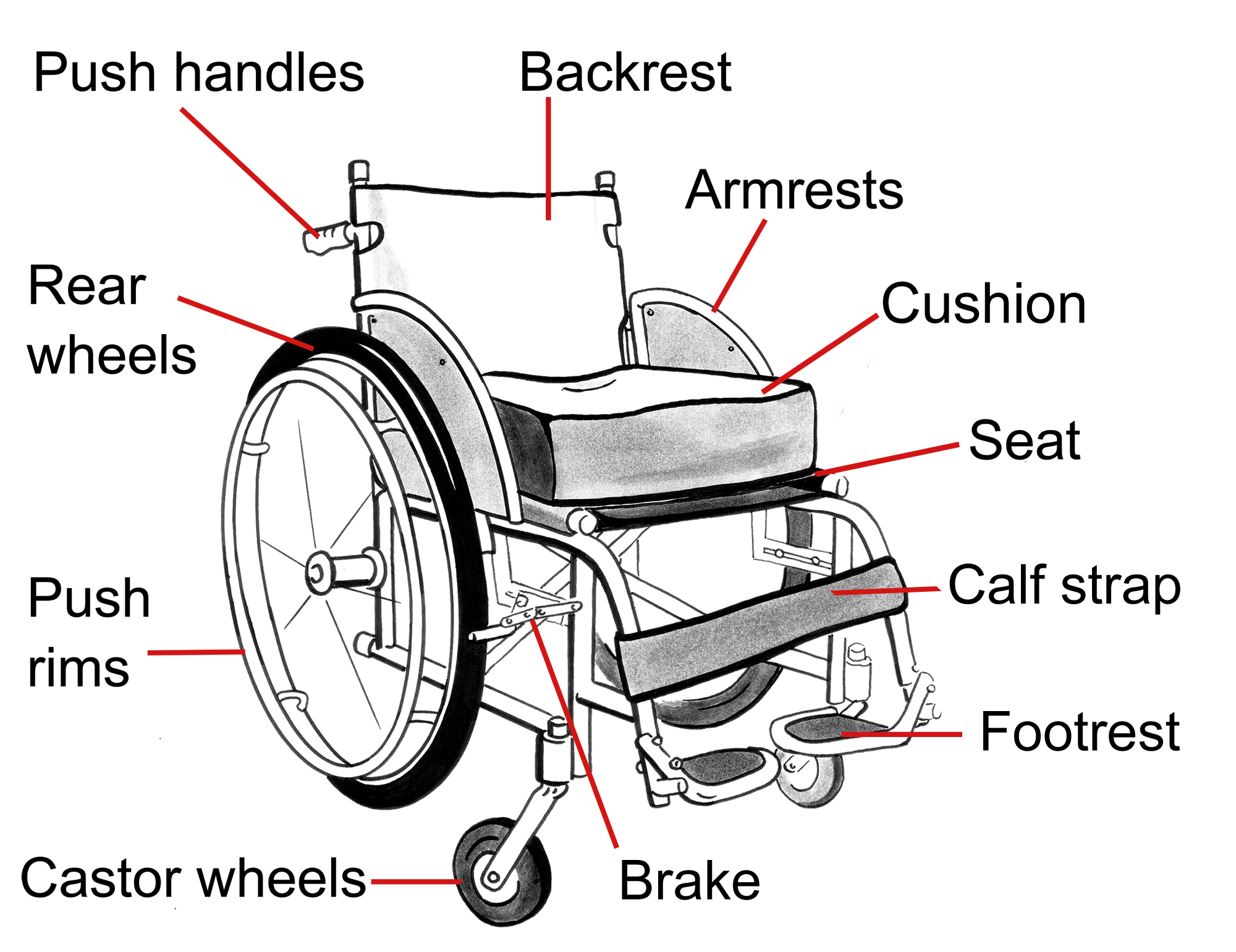
A wheelchair assists a person to move from one place to another while seated.
All wheelchairs have some important features.
Important features
To be safe and effective, all wheelchairs should:
- Be strong and durable
- Have a smooth finish to prevent injury
- Be available in different sizes
- Have brakes
- Have height adjustable footrests and a calf or ankle strap
- Have a cushion
- Be specified to carry the weight of the user.
Features to consider for emergencies
To speed up service provision, consider wheelchairs that are:
- Quick to assemble
- Simple to adjust and fit.
Wheelchairs for temporary wheelchair users may be less adjustable than wheelchairs for long term wheelchair users.
The ground in emergency conditions can often be rough or uneven. Consider wheelchair features that are made for rough ground:
- Thick tyres
- Puncture proof inner tubes
- Large castor wheels
- Long distance between the centres of the rear wheel and castor wheel (wheelbase).
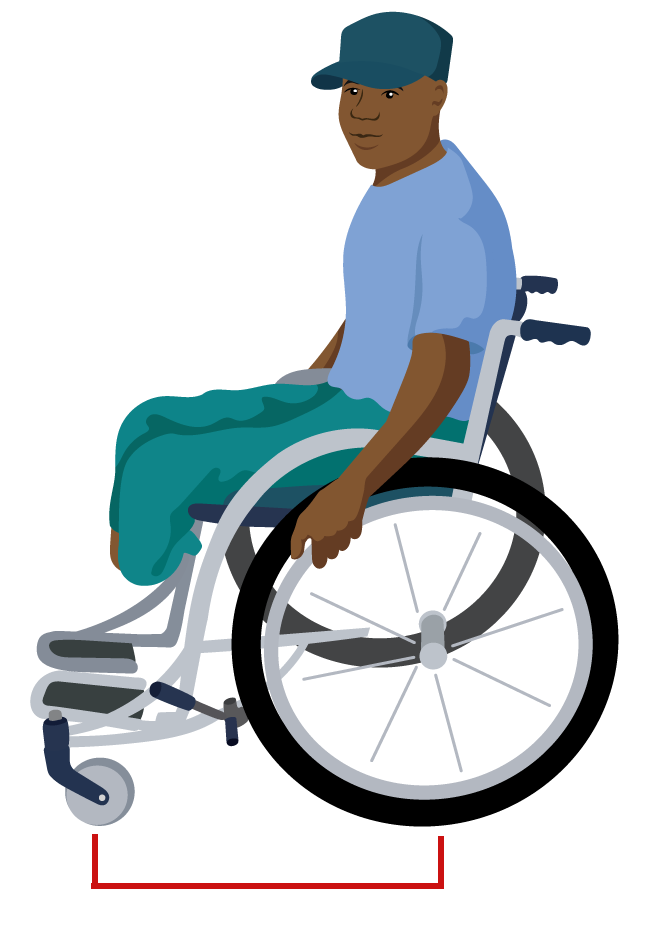

Long wheelbase
Other adjustable features
Push handle:
- Used by a person who is assisting
- Can be adjusted in height but should not get in the way when the person is propelling.
Rear wheel, push rim and castor wheel:
- Used to propel the wheelchair
- Larger castor wheels may be easier to propel on rough ground.
Backrest and seat:
- To support a person to sit well in the wheelchair (always with a cushion)
- Different sizes are important to fit people of different heights.
Armrest:
- Used to push up from when standing up
- Protects a person’s clothing from dirt
- Can be flip up or removable.

Backrests
Backrests can come in different heights:
- A higher backrest offers a person more support
- A lower backrest offers a person more freedom in the shoulders to propel more easily.

Meet Maria
Maria has multiple sclerosis, which is a condition that affects the nerves in the brain and spinal cord.
She has difficulty sitting without support and uses a high backrest.

Remember Peter?
Peter is fit and active and benefits from a low backrest that gives him freedom to move and propel efficiently.
Question
Which of the following people may benefit from a lower backrest position?
Select all that apply.
A person who is:
If you selected b, d and e, you are correct!
People who are fit and active and can sit well without support benefit from a lower backrest position which gives them freedom in their shoulders to propel efficiently. Very short people may also benefit from a lower backrest position.
a, c and f are incorrect.
People who get tired quickly, or have difficulty sitting well without support benefit from the extra support of a high backrest. Very tall people may also benefit from a higher backrest position.
Rear wheels
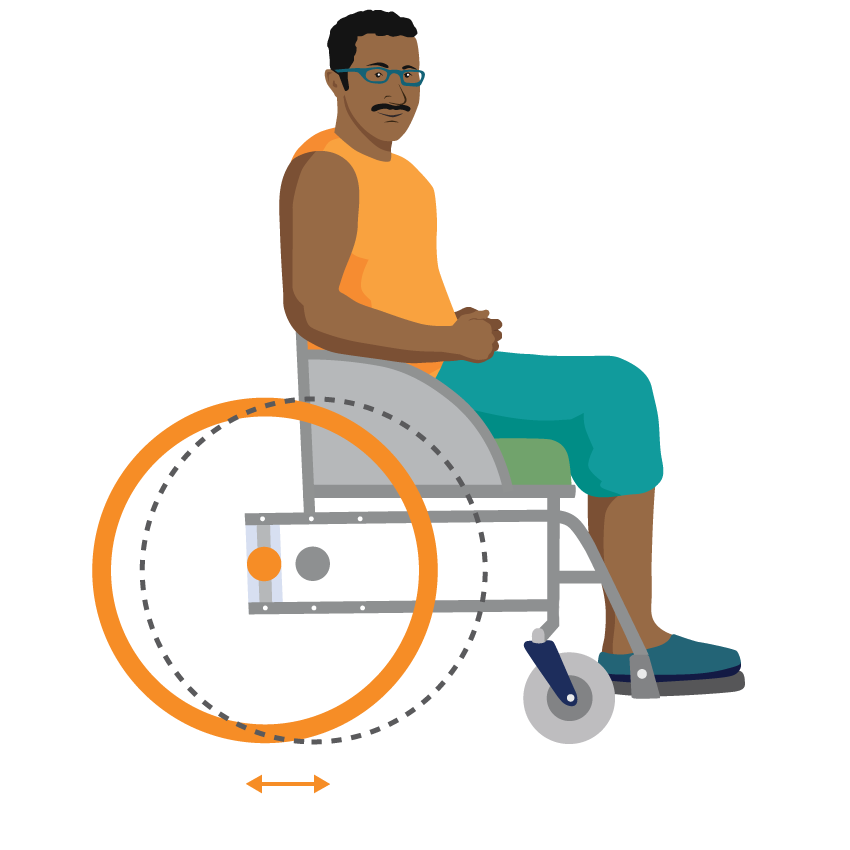
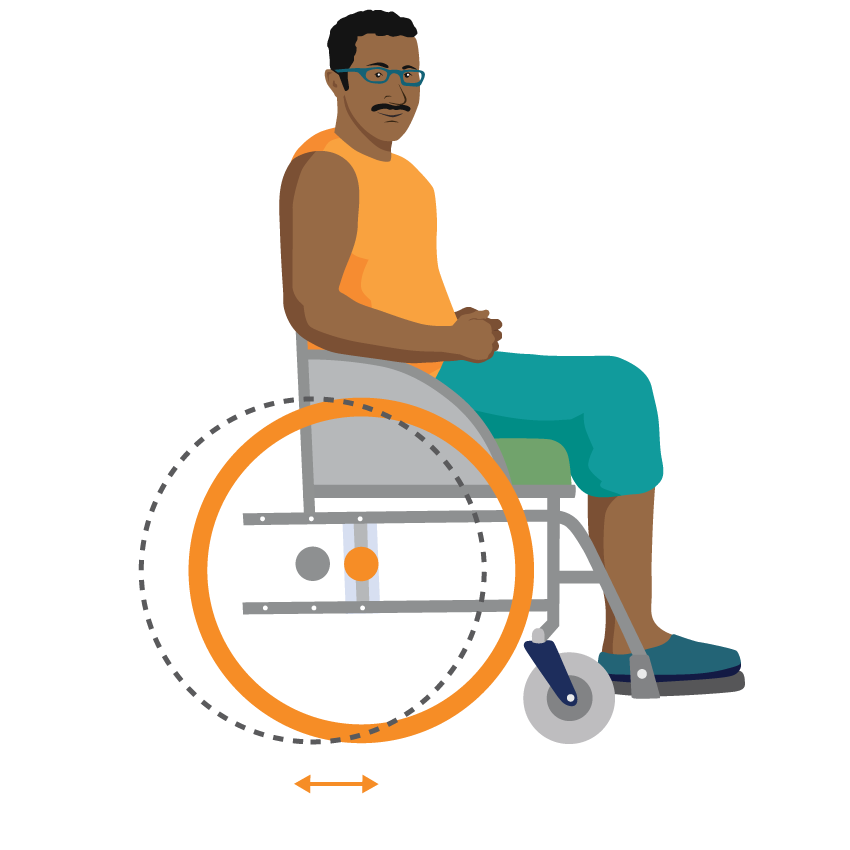
Some wheelchairs offer a choice of different rear wheel positions.
Safe rear wheel position makes the wheelchair more stable when going up and down slopes but feels heavier to propel. The rear wheel is further back relative to the person.
Active rear wheel position makes the wheelchair less stable going up and down slopes but feels easier to propel. The rear wheel is further forward relative to the person.
Safe rear wheel position
Active rear wheel position
Question
Which of the following people may benefit from a more stable (safer) rear wheel position?
Select all that apply.
A person who is:
If you selected c, d, e and f, you are correct!
A person may feel unstable going up or down slopes if they have limb loss, or are very tall, experience sudden uncontrolled movements or are feeling anxious about propelling a wheelchair.
a, b and g are incorrect.
People who are active or can do a wheelie, or are very short will benefit from a wheelchair which is lighter and more active to propel.
Features for transferring
We have looked at how backrest height and rear wheel position affect propelling.
Let us look more closely at the wheelchair features important for transferring.
Watch this video of a person transferring from a wheelchair.
Question
Which features are most important to consider when transferring?
If you selected c, g and j, you are correct!
The most important features to consider are footrests, armrests and brakes.
Footrests, armrests and brakes can be an obstacle during transfers. Moving them out of the way may make transfers easier. Brakes are important for keeping the wheelchair still and safe while transferring.
a, b, d, e, f, h, i and k are incorrect.
Discussion
Look at the available wheelchairs. Do they have removable or flip up footrests and / or armrests?
Features for sitting upright
Complete this activity to learn more about which features are important for a person to sit in an upright and comfortable position.
Activity
In groups, take turns to sit in a wheelchair and discuss the most important features that are supporting you to be comfortable and sit upright.

If you selected b, d, e, f and g, you are correct!
The backrest, cushion and seat are the main features supporting a person’s body and upper leg/s.
The footrest and calf strap are the main features supporting a person’s lower leg and feet.
These features help a person to sit upright.
a, c, h, i, j and k are incorrect.
Difficulty sitting upright
It is not possible for everyone to sit upright in a basic wheelchair.
Some people need extra support in their wheelchair or a dedicated supportive seat.
This helps them to sit safely and comfortably.
Cushions
Every wheelchair should have a cushion.
Two types of cushion are needed in emergency situations:
- A comfort cushion helps a person to sit in more comfort when using the wheelchair
- A pressure relief cushion provides extra pressure relief and protection for a person at risk of developing pressure wounds.
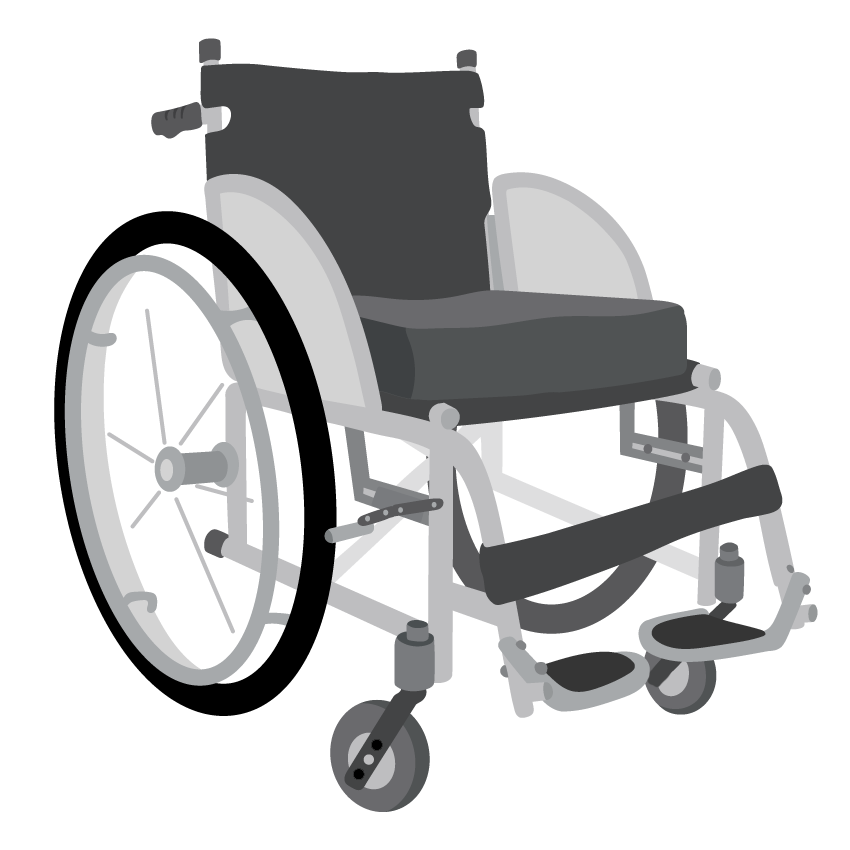

Wheelchair with comfort cushion
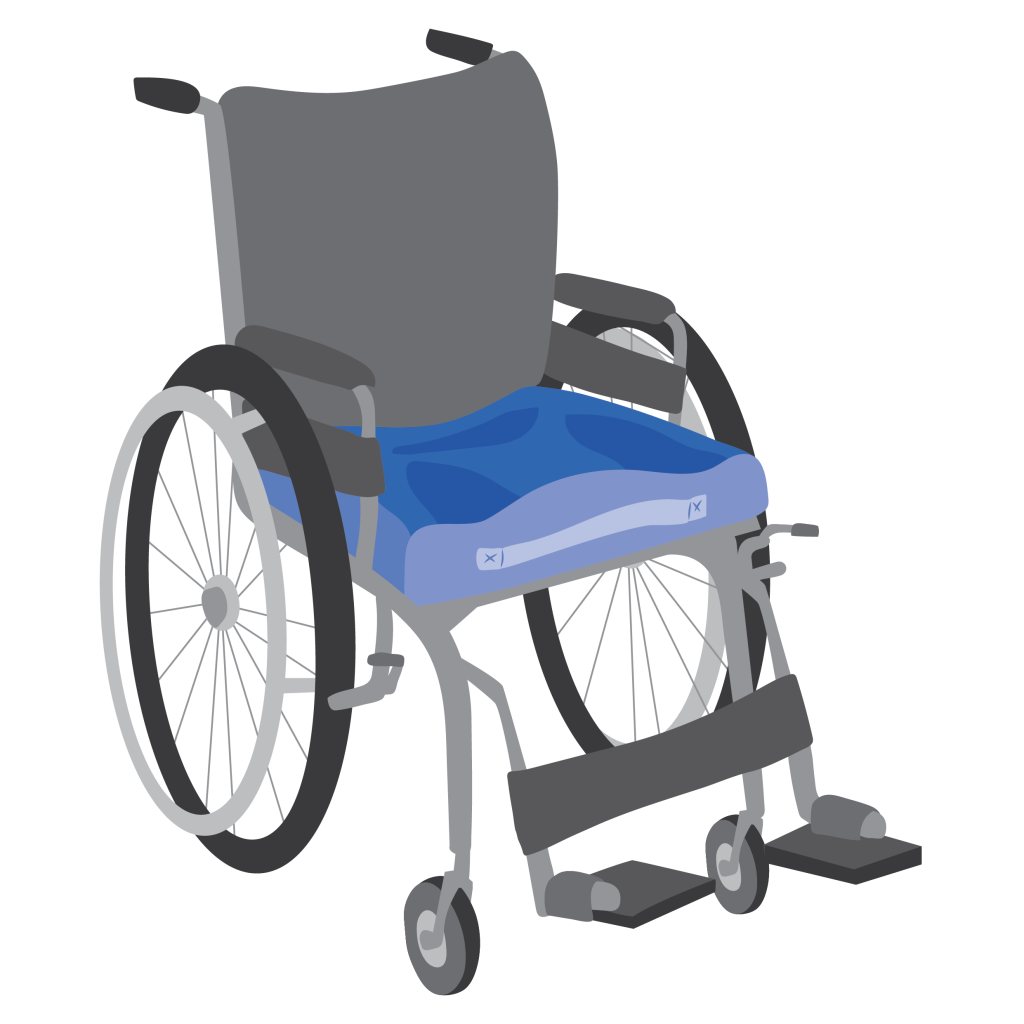

Wheelchair with pressure relief cushion
Read on to learn about pressure wounds.
Pressure wounds
A pressure wound is a breakdown of a person’s skin. It is usually over a bony area such as their back, hips or seat bones.
A mark on the person’s skin is the first sign of a pressure wound:
- If a person has light colour skin, the mark will be red.
- If a person has dark colour skin the mark will be blue/purple.
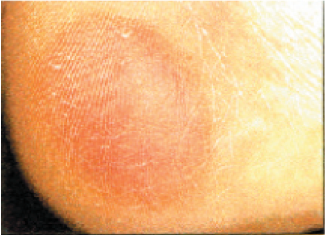
Stage one
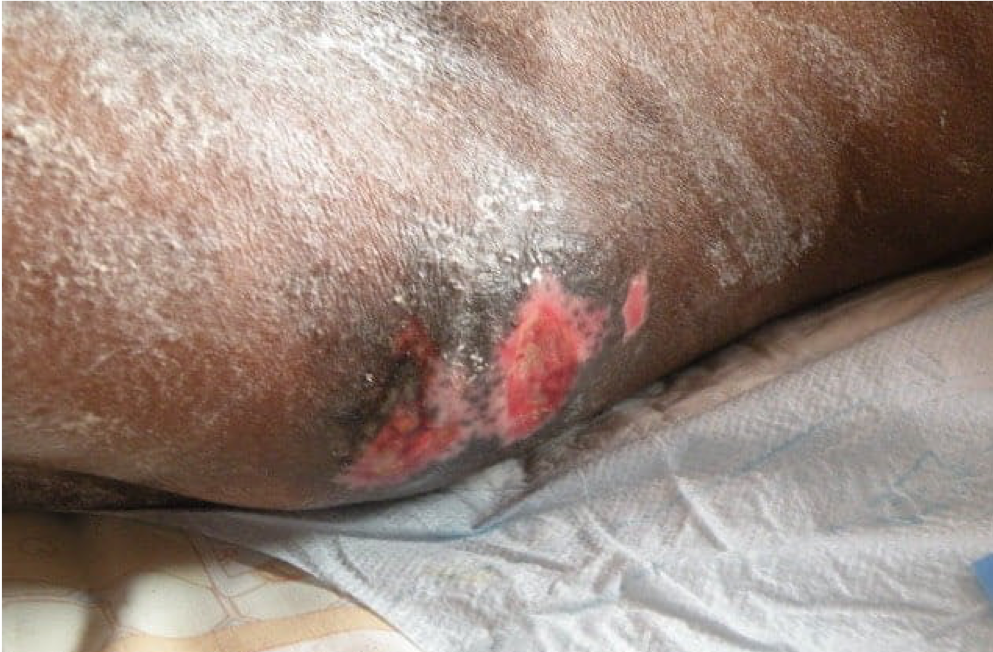
Stage two
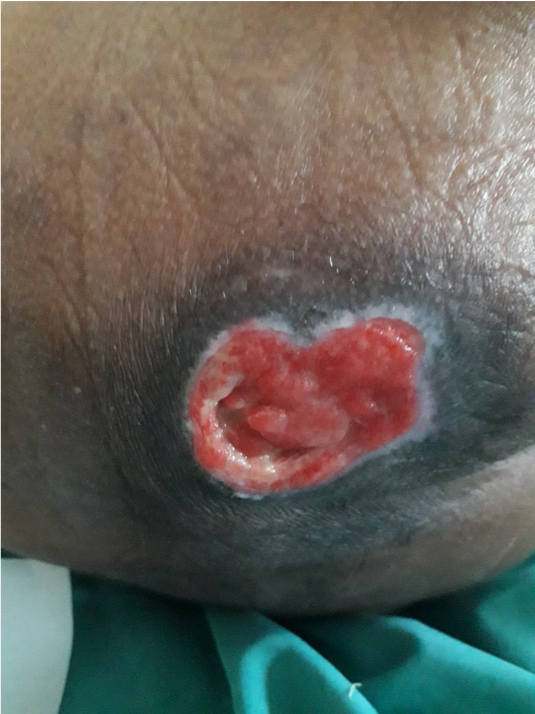
Stage three
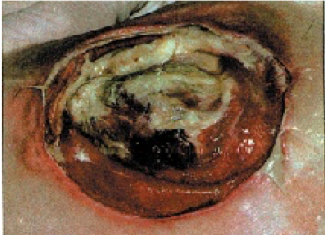
Stage four
Pressure wounds are a common problem for people with loss of feeling (sensation) or difficulty moving and changing position.
If someone has had a wound before they are at risk of another wound.
Discussion
Think of a person you know who has had a pressure wound. If you don’t know anyone, speak to others and see if they can think of someone?
Did the person have:
- A loss of feeling (sensation)?
- Difficulty moving or changing position?
- A pressure wound in the past?
- Another reason for developing the wound?
Anyone at risk of pressure wounds should have a pressure relief cushion.
If a person has an existing pressure wound, they should be referred to a health professional for a wound assessment.
Learn more about pressure wounds in the TAP Mobility assistive products module.
Second pressure relief cushion
If a person experiences leaks from their bladder or bowel their cushion may get wet or soiled.
Skin damage can happen quickly and wounds may develop.
A second pressure relief cushion can help the person to continue using their wheelchair while washing and drying their other cushion and cover.
If a person has difficulty with leaks, they should be referred for continence assessment.
Learn more about skin care in the TAP Absorbent products module.
Optional features
Leg raiser
A leg raiser is an option that can be added to a wheelchair to raise a person’s leg and help reduce swelling after an injury or surgery.
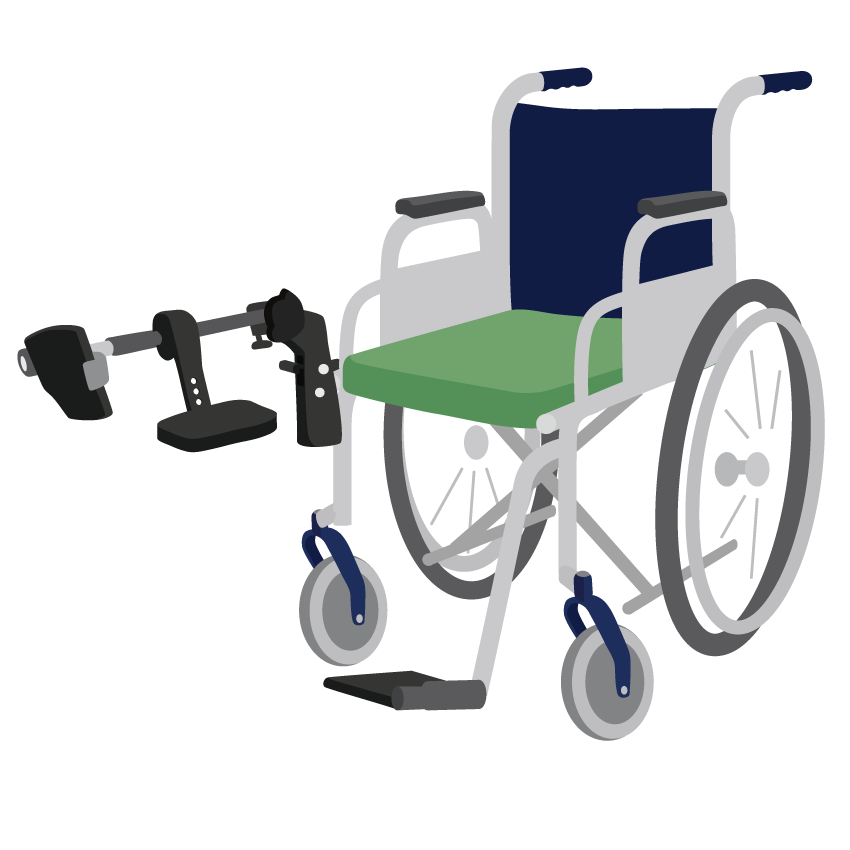

Stump board
A stump board is an option that can be added to a wheelchair to support a person with an amputation below their knee after surgery.
The stump board keeps the knee in an extended (straight) position and helps to prevent the muscles at the back of the knee becoming tight. This is important for walking well with a prosthetic leg in the future.
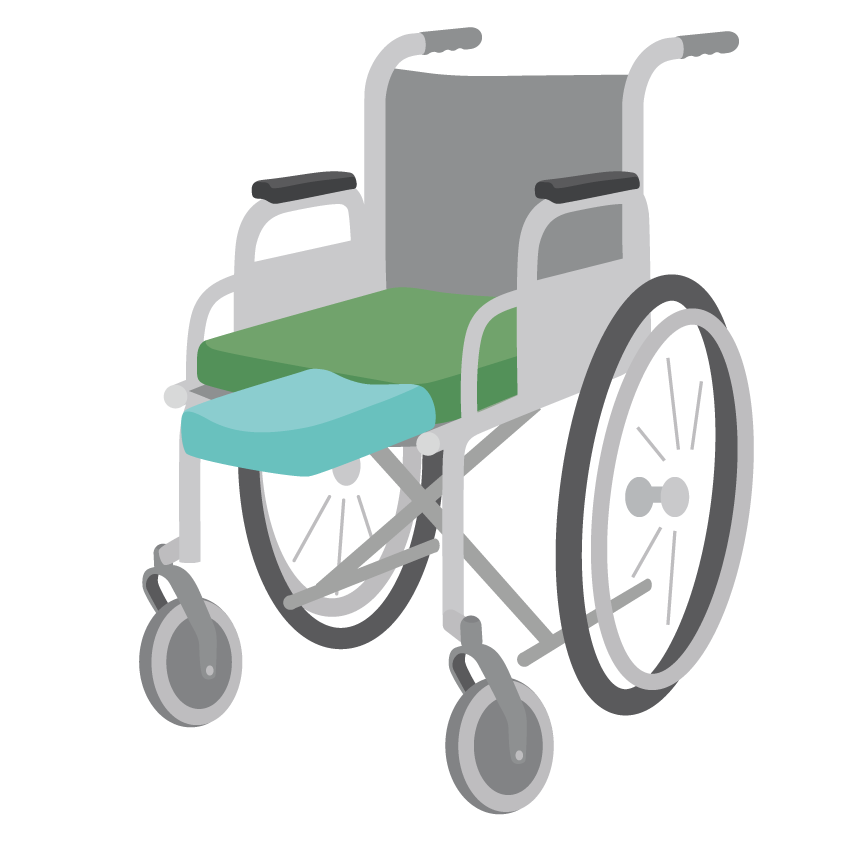

Supportive seating
A person may benefit from supportive seating because they need extra support to sit upright.
Extra support helps a person who has difficulty sitting upright in four ways:
- Improving balance, posture and stability
- Improving comfort
- Helping to prevent pressure wounds
- Slowing down or preventing problems with posture in the future.
A wheelchair with supportive seating needs to be provided by staff who have had advanced training.
Wheelchairs with supportive seating are not included in TAP.
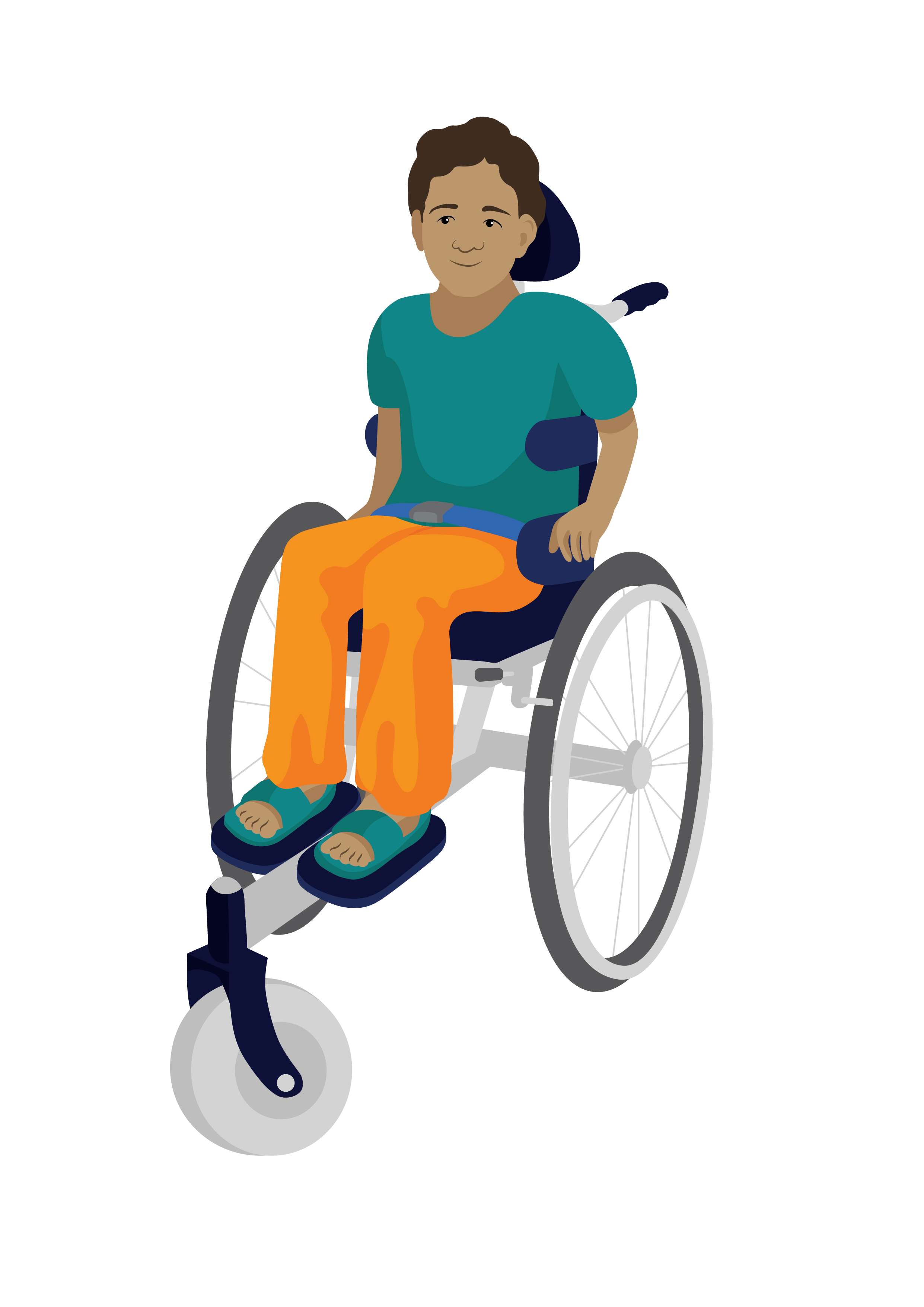
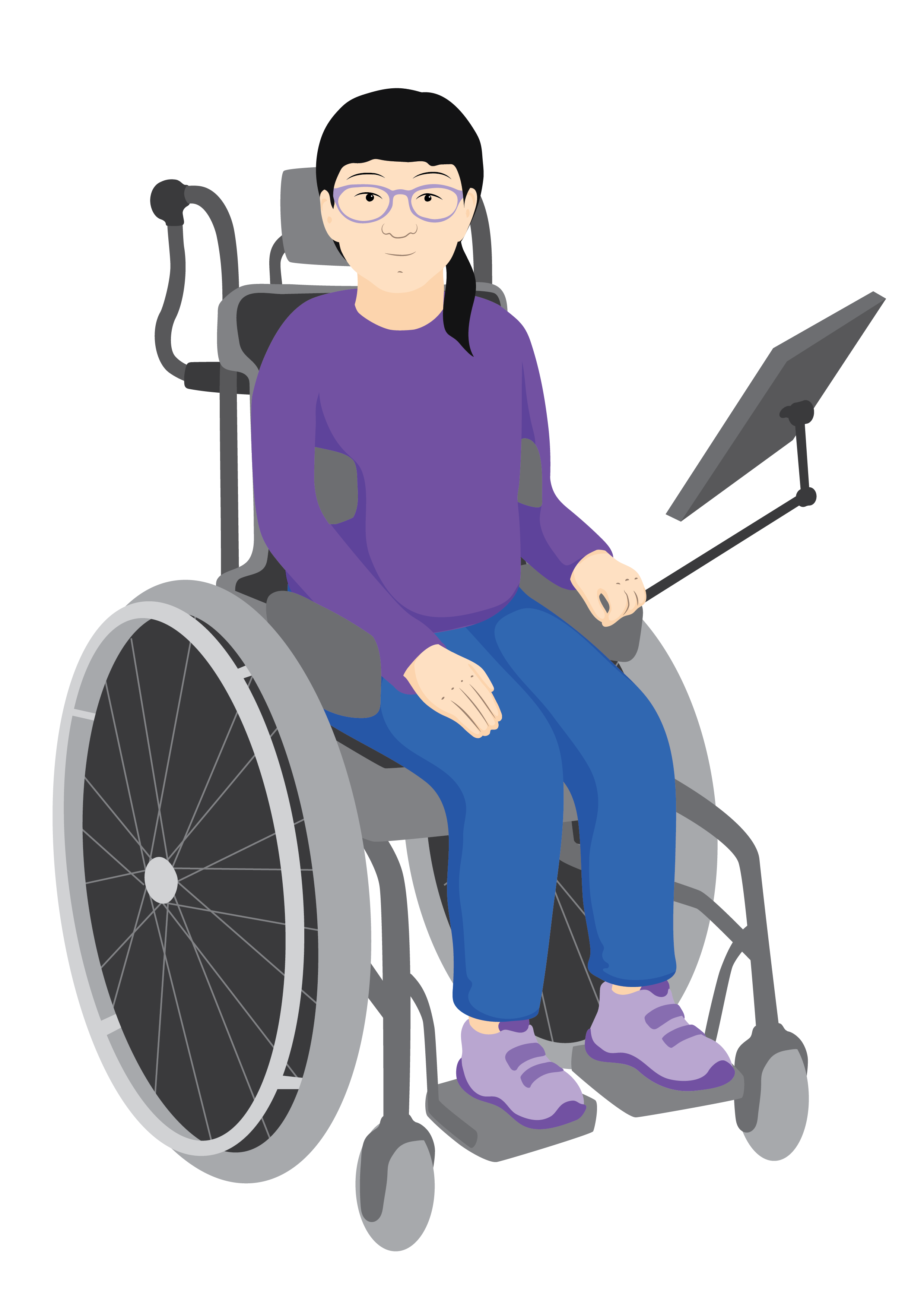


It is important to recognise when a person needs extra support so they can be referred.
Find out about how to identify who needs supportive seating in Lesson two.