О сайте
Обучение на TAP (сокращенно TAP) - это инновационный ресурс ВОЗ для смешанного обучения. На нашей платформе с открытым доступом размещены модульные онлайн-курсы по целому ряду тем в области здравоохранения. Курсы предназначены для онлайн-обучения с последующим очным обучением и практикой под наблюдением на рабочем месте. TAP обеспечивает подготовку работников первичного звена здравоохранения и общин, а также программы дослужебного образования. Цель - расширить доступ к услугам первичного и общинного здравоохранения для людей, которые в них нуждаются.

Для кого это?

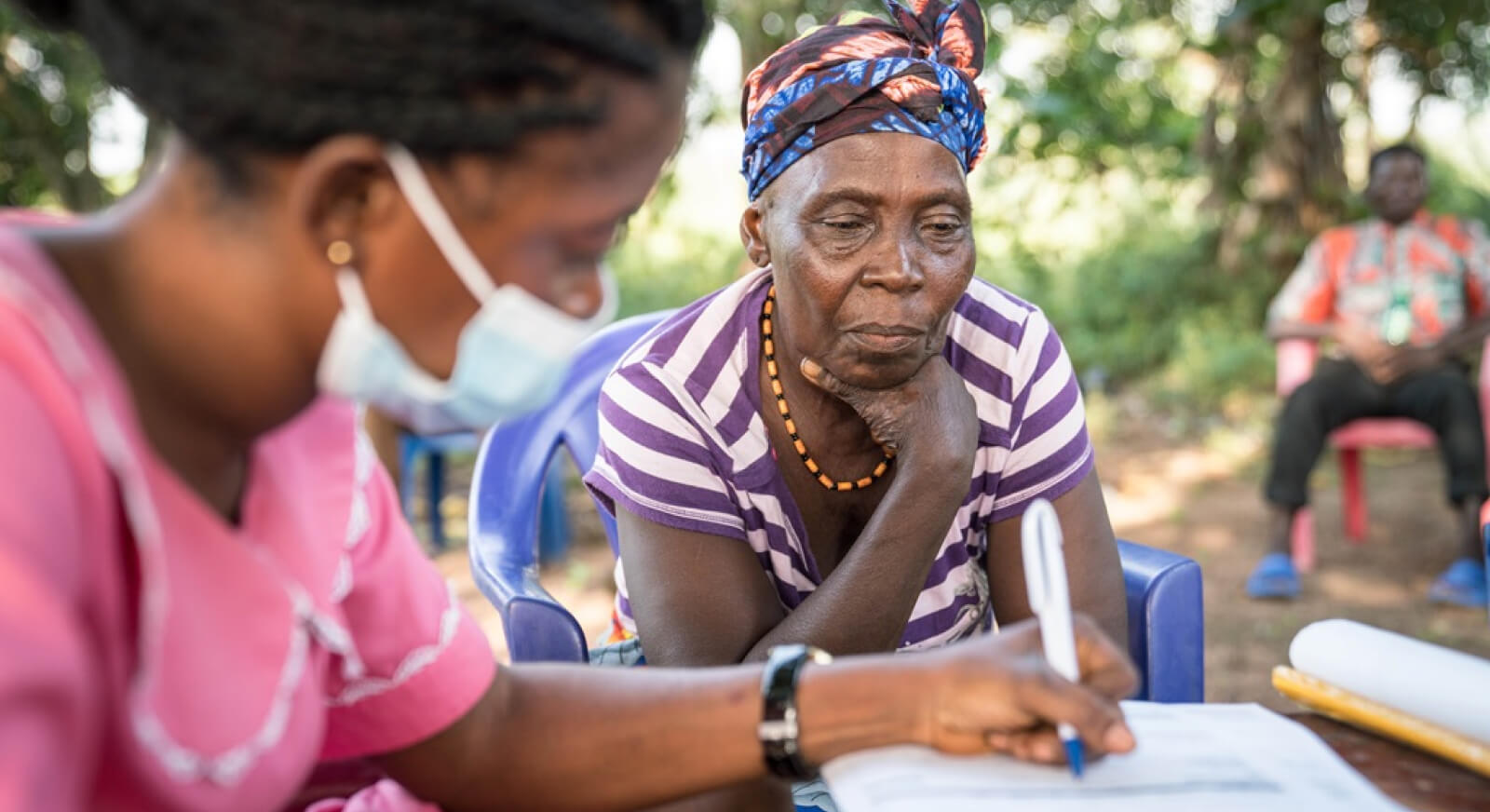
Персонал первичной медико-санитарной помощи
К ним относятся врачи, медсестры, помощники медсестер, фармацевты и работники здравоохранения на уровне общин.Люди, работающие в обществе
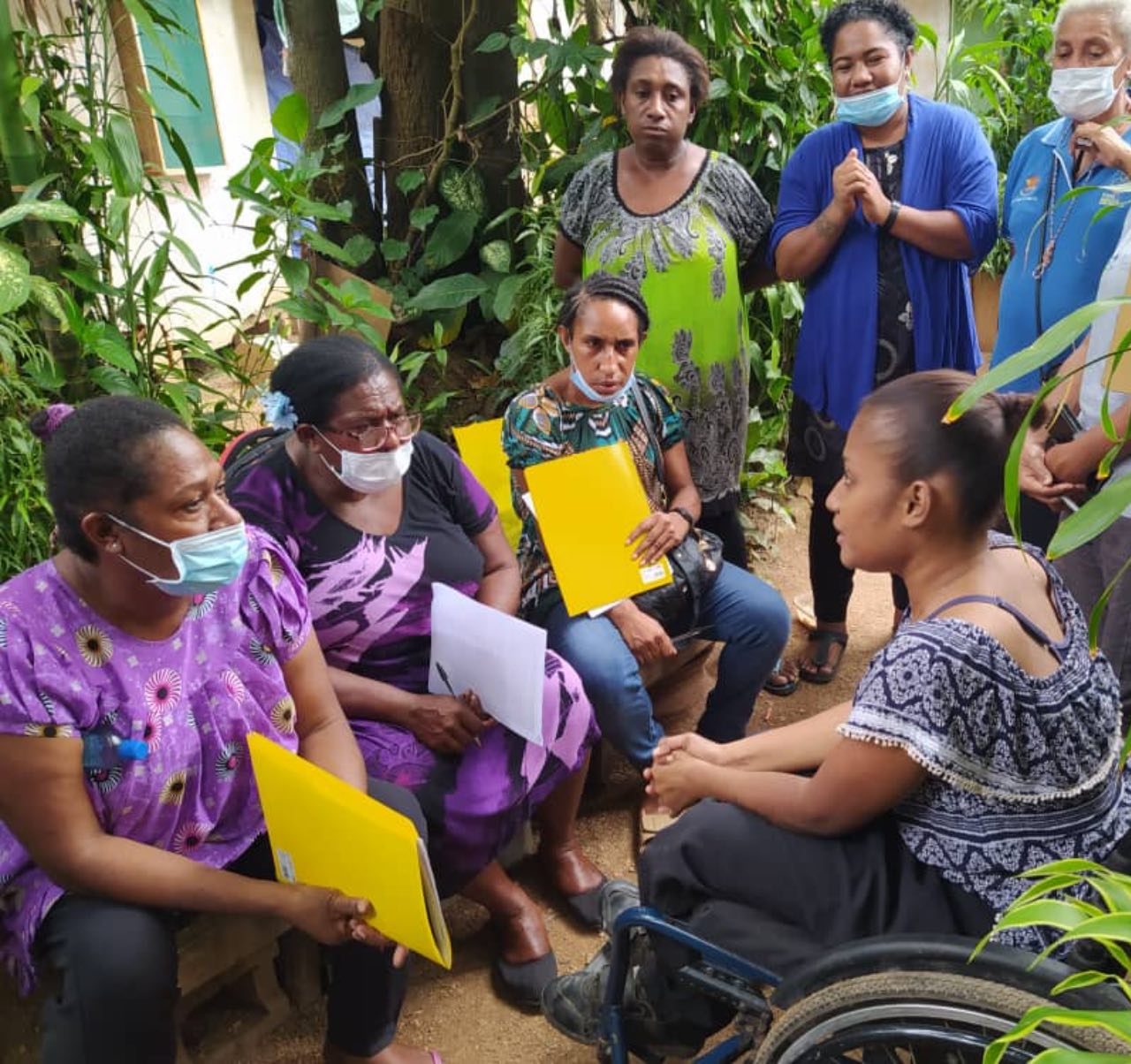
К ним относятся люди, работающие в сфере образования, социальных услуг или здравоохранения.Предварительная подготовка
Курсы можно использовать для составления учебных планов в рамках программ дослужебной подготовки и образования. Содержание курсов также может быть использовано при разработке учебных программ.Как это работает
Начать обучение очень просто. Просто зарегистрируйтесь, войдите в систему и погрузитесь в курс.
Регистрация
Создайте свою учетную запись, чтобы получить доступ ко всему спектру курсов и ресурсов.
Создайте свой аккаунтВход в систему
Войдите в систему в любое время, чтобы получить доступ к вашей персональной панели управления.
Вход в системуУчиться онлайн
Изучите разнообразные курсы, отвечающие вашим личным и профессиональным целям.
Изучите курсыОсобенности платформы
Курсы
- Курсы с цветовой кодировкой для удобной навигации
- Углубленные модули для расширения ваших знаний и навыков
- Интерактивные элементы, способствующие вовлечению в изучение тем
- Доступны на разных языках.

Интерактивный
Викторины и сертификаты
- Отслеживайте свой прогресс
- Испытайте себя в реальных сценариях
- Зарабатывайте загружаемые сертификаты.


Библиотека ресурсов
- Видеоролики с отзывами и учебными материалами
- Формы скрининга и оценки и вспомогательные документы
- Ресурсы для местных наставников и исполнителей.
Вкладчики
Концепция и разработка:Ирен Кальво, Каролина Дер Мусса, Сара Фрост, Люси Норрис, Джулия Оггеро, Люси Паннелл, Луиза Пули, Кайли Шай, Эмма Теббатт, Миташа Ю.
Доступность: Петр Зролка, Селин Хазбун.
Иллюстрации, графика и медиа:Коди Эш, Джордан Бэнг, Джули Десноулз, Эйнсли Хэдден, Соломон Гебби.
Сайт:Физиопедия.
Партнеры по исследованиям, разработкам и внедрению:Медицинский колледж Баттерджи, Саудовская Аравия; HelpAge Tanzania, Танзания; Humanity and Inclusion, Ирак; Human Study e.V, Германия; Индийский институт общественного здравоохранения; Международный комитет Красного Креста, Швейцария; Mobility India, Индия; Министерство здравоохранения, Бутан; Министерство здравоохранения, Украина; Motivation Australia, Австралия; Motivation Romania, Румыния; Медицинский колледж Маулана Азад, Индия; Управление здравоохранения провинции Национального столичного округа, Папуа - Новая Гвинея;Национальный институт физической медицины и реабилитации, Индия; Национальная служба ортопедии и протезирования, Папуа - Новая Гвинея; Papua New Guinea Eye Care; Глазная клиника Главной больницы Порт-Морсби, Папуа - Новая Гвинея; Rural Development Trust, Индия; Society for Sound Hearing, Индия; University of Southampton, Великобритания.
Страновые бюро ВОЗ в:Азербайджане, Бутане, Эфиопии, Фиджи, Грузии, Гане, Индии, Индонезии, Ираке, Иране (Исламской Республике), Либерии, Мьянме, Непале, Пакистане, Папуа - Новой Гвинее, Румынии, Таджикистане, Украине, Объединенной Республике Танзания.
Региональные бюро ВОЗ:Региональное бюро для Африки, Региональное бюро для Северной и Южной Америки, Региональное бюро для Восточного Средиземноморья, Региональное бюро для Европы, Региональное бюро для Юго-Восточной Азии, Региональное бюро для западной части Тихого океана.
Разработка модулей:В разработке каждого модуля принимали участие многие заинтересованные стороны и использовались исходные материалы. Информация об этих людях и организациях приводится в конце каждого модуля.
Финансовая поддержка: Благодарим следующие организации за щедрую финансовую поддержку: Программа AT2030 UKAID под руководством GDI Hub, правительства Норвегии и Австрии, Агентство США по международному развитию (USAID), Глобальное партнерство по вспомогательным технологиям ATscale, организованное Управлением ООН по обслуживанию проектов (UNOPS), Управление ООН по координации гуманитарных вопросов (UNOCHA).